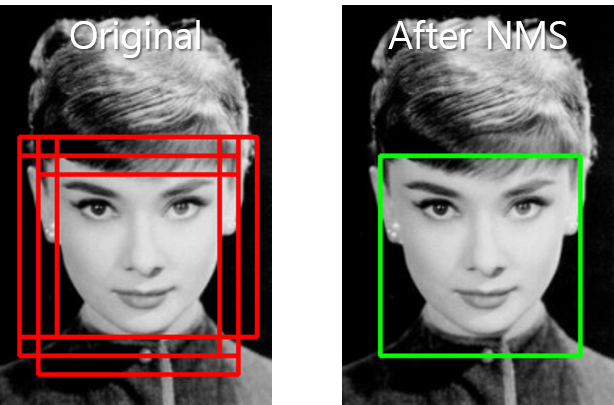
YOLO와 같은 Object detection을 구현하다보면 하나의 Object에 대한 복수의 Detection이 가능하다. 이는, Object detection의 정확도를 떨어뜨릴 수 있는 요소이기 때문에 해결해 주어야하는데 이를 위해 사용되는 방법이 Non-Maximum Suppression(NMS)이다. NMS는 YOLO post에서도 언급을 했었는데, 핵심 아이디어는 다음과 같이 간단하다.
- 주어진 Box들 중 가장 높은 Score를 가진 Box를 선택한다.
- 선택된 Box와 나머지 Box들간의 iou(interaction of union)을 계산하고 특정값(iou threshold) 이상이면 제거한다.(동일한 Object에 대한 Detection이기 때문에 겹치는 부분이 많을 것이라는 생각)
- 특정한 Box의 숫자가 남을 때까지나 더이상 선택할 Box가 없을 때까지 위의 과정을 반복한다.
위의 과정을 통해 최대한 하나의 Object에 하나의 Detection box만이 존재하도록 만들게 된다. 이 아이디어는 이미 Tensorflow에 tf.image.non_max_suppression으로 구현되어있기에 우리가 직접 구현할 필요는 없지만 보다 확실한 이해를 위해서 다음과 같이 Python code로 구현해볼 수 있다.
NMS 구현
# Felzenszwalb et al
def non_max_suppression_fast(boxes, scores, iou_threshold):
'''
boxes : coordinates of each box
scores : score of each box
iou_threshold : iou threshold(box with iou larger than threshold will be removed)
'''
if len(boxes) == 0:
return []
# Init the picked box info
pick = []
# Box coordinate consist of left top and right bottom
x1 = boxes[:,0]
y1 = boxes[:,1]
x2 = boxes[:,2]
y2 = boxes[:,3]
# Compute area of each boxes
area = (x2 - x1 + 1) * (y2 - y1 + 1)
# Greedily select the order of box to compare iou
idxs = np.argsort(scores)
while(len(idxs) > 0):
last = len(idxs) - 1
i = idxs[last]
pick.append(i)
# With vector implementation, we can calculate fast
xx1 = np.maximum(x1[i], x1[idxs[:last]])
yy1 = np.maximum(y1[i], y1[idxs[:last]])
xx2 = np.minimum(x2[i], x2[idxs[:last]])
yy2 = np.minimum(y2[i], y2[idxs[:last]])
w = np.maximum(0, xx2 - xx1 + 1)
h = np.maximum(0, yy2 - yy1 + 1)
intersection = w * h
# Calculate the iou
iou = intersection / (area[idxs[:last]] + area[idxs[last]] - intersection)
idxs = np.delete(idxs, np.concatenate(([last], np.where(iou > iou_threshold)[0])))
return boxes[pick].astype("int")
위와 같은 방식을 통해 NMS를 구현하고 box의 coordinate, score 그리고 iou_threshold를 잘 설정해준다면 우리가 원하는대로 object가 서로 겹치지 않는 box들의 집합을 얻을 수 있다.
Ref
- https://www.pyimagesearch.com/2015/02/16/faster-non-maximum-suppression-python/